How Well Do You Understand Retirement Plan Rules?
By Mark FisselPosted on April 30th, 2021
Qualified retirement plans, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, have many rules, and some of them can be quite complicated. Take the following quiz to see how well you understand some of the finer points.
1. You can make an unlimited number of retirement plan rollovers per year.
A. True
B. False
C. It depends
2. If you roll money from a Roth 401(k) to a Roth IRA, you can take a tax-free distribution from the Roth IRA immediately as long as you have reached age 59½.
A. True
B. False
C. It depends
3. You can withdraw money penalty-free from both your 401(k) and IRA (Roth or traditional) to help pay for your children’s college tuition or to pay for health insurance in the event of a layoff.
A. True
B. False
C. It depends
4. If you retire or otherwise leave your employer after age 55, you can take penalty-free distributions from your 401(k) plan. You can’t do that if you roll 401(k) assets into an IRA.
A. True
B. False
C. It depends Shares of Traditional IRA Assets Opened with…
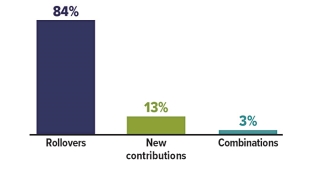
Source: Investment Company Institute, 2020 (data reflects IRAs opened in 2016)
1. C. It depends. Rollovers can be made in two ways — through a direct rollover, also known as a trustee-to-trustee transfer, in which you authorize the funds to be transferred directly from one account or institution to another, or through an indirect rollover, in which you receive a check in your name (less a required tax withholding) and then reinvest the full amount (including the amount withheld) in a tax-deferred account within 60 days. If the full amount is not reinvested, the outstanding amounts will be considered a distribution and taxed accordingly, including any applicable penalty. Generally, individuals can make an unlimited number of rollovers in a 12-month period, either direct or indirect, involving employer-sponsored plans, as well as an unlimited number of direct rollovers between IRAs; however, only one indirect (60-day) rollover between two IRAs is permitted within a 12-month period.
2. C. It depends. Beware of the five-year rule as it applies to Roth IRAs. If you establish your first Roth IRA with your Roth 401(k) rollover dollars, you will have to wait five years to make a qualified withdrawal from the Roth IRA, regardless of how long you’ve held the money in your Roth 401(k) account, even if you are over 59½. However, if you have already met the five-year holding requirement with any Roth IRA, you may take a tax-free, qualified withdrawal.
3. B. False. You can take penalty-free withdrawals from an IRA, but not from a 401(k) plan, to pay for a child’s qualifying education expenses or to pay for health insurance premiums in the event of a job loss. Note that ordinary income taxes will still apply to the taxable portion of the distribution, unless it’s from a Roth account that is otherwise qualified for tax-free withdrawals.
4. A. True. If you leave your employer after you reach age 55, you may want to consider carefully whether to roll your money into an IRA. Although IRAs may offer some advantages over employer-sponsored plans — such as a potentially broader offering of investment vehicles — you generally cannot take penalty-free distributions from an IRA between age 55 and 59½, as you can from a 401(k) plan if you separate from service. If you might need to access funds before age 59½, you could leave at least some of your money in your employer plan, if allowed.
When leaving an employer, you generally have several options for your 401(k) plan dollars. In addition to rolling money into an IRA and leaving the money in your current plan (if the plan balance is more than $5,000), you may be able to roll the money into a new employer’s plan or take a cash distribution, which could result in a 10% tax penalty (in addition to ordinary income taxes) on the taxable portion, unless an exception applies.
Source: Broadridge